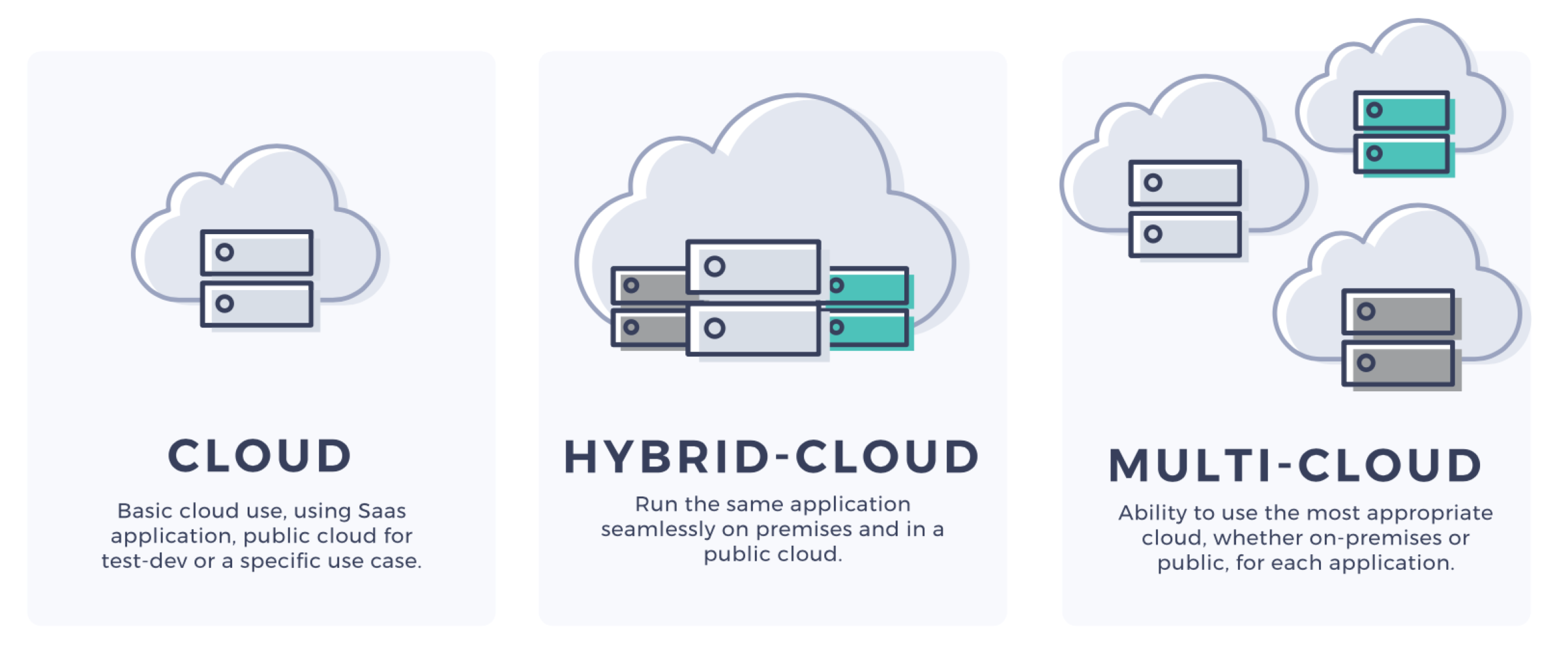
Understanding Multi-Cloud Computing: A Strategic Approach to Modern IT Infrastructure
Multi-cloud computing refers to the use of multiple cloud service providers to deploy and manage applications and data. Unlike single-cloud strategies, multi-cloud allows organizations to leverage various platforms such as AWS, Azure, Google Cloud, and others, to optimize performance, cost, and resilience. This approach enables businesses to avoid vendor lock-in, improve redundancy, and tailor solutions to specific needs. By distributing workloads across different clouds, companies can enhance flexibility and adapt to changing demands efficiently. The multi-cloud model is gaining popularity as it aligns with digital transformation goals, providing scalable, reliable, and cost-effective infrastructure. It also helps organizations mitigate risks associated with reliance on a single provider, ensuring continuity even if one platform experiences outages or issues.
Advantages of Multi-Cloud Computing
Implementing multi-cloud strategies offers numerous benefits. It provides enhanced flexibility, allowing organizations to select the best services from various providers based on features, pricing, and compliance requirements. Multi-cloud also bolsters resilience, as workloads are distributed across multiple environments, reducing the impact of outages. Cost optimization is another key advantage, enabling businesses to choose the most cost-effective options for specific tasks. Additionally, multi-cloud enhances performance by deploying workloads closer to end-users or specific data sources. It also facilitates compliance with diverse regulatory standards across different regions, ensuring data sovereignty and security. Overall, this approach enables organizations to innovate rapidly, adapt quickly to market changes, and maintain a competitive edge.
Challenges in Multi-Cloud Implementation
Despite its benefits, multi-cloud computing presents several challenges. Managing multiple cloud platforms requires sophisticated tools and expertise to handle complex integrations and orchestration. Security becomes more complicated as organizations must ensure consistent policies across providers and protect data in diverse environments. Cost management can also be challenging due to varying pricing models and hidden expenses. Additionally, data portability and interoperability issues may arise, making migration and workload transfer difficult. Governance and compliance require careful planning to meet regional and industry-specific standards. Lastly, organizations need skilled personnel familiar with multiple cloud ecosystems. Addressing these hurdles involves investing in advanced management tools, robust security protocols, and comprehensive training to fully realize multi-cloud benefits.
Key Technologies Enabling Multi-Cloud Strategies
Several technologies are foundational to effective multi-cloud deployments. Cloud management platforms (CMPs) provide centralized control, automation, and orchestration across multiple clouds. Containerization tools like Docker and Kubernetes facilitate portability and consistent deployment environments, simplifying workload migration. API-driven architectures enable seamless integration and communication between different cloud services. Hybrid cloud solutions combine on-premises infrastructure with multiple clouds, offering greater flexibility. Identity and access management (IAM) systems ensure secure and unified user access across platforms. Additionally, monitoring and analytics tools help organizations track performance, optimize resource utilization, and troubleshoot issues. These technologies collectively empower organizations to build resilient, scalable, and manageable multi-cloud environments aligned with their strategic objectives.
Future Trends in Multi-Cloud Computing
The future of multi-cloud computing is poised for continued evolution driven by emerging trends. Artificial intelligence and machine learning will increasingly enhance automation, predictive analytics, and security across multi-cloud environments. Edge computing is expected to integrate seamlessly, enabling real-time data processing closer to end devices. Multi-cloud security will become more sophisticated with unified threat detection and automated response systems. Moreover, industry-specific cloud solutions tailored for healthcare, finance, and other sectors will expand, offering specialized compliance and functionalities. As organizations aim for greater agility, hybrid and multi-cloud architectures will become more streamlined and easier to manage. Overall, multi-cloud computing will remain a critical strategy for organizations seeking innovation, resilience, and competitive advantage in an increasingly digital world.